Workplace hazardous materials are not just a safety concern — they’re a legal matter.
Under WHMIS 2025 compliance requirements, both employers and employees have defined duties. Failing to meet them can lead to severe consequences, including fines, stop-work orders, or even criminal charges.
Let’s break down exactly what employer responsibility under WHMIS means, what employer WHMIS training obligations entail, and how you can keep your workplace compliant.
Understanding WHMIS 2025
WHMIS (Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System) sets the standards for identifying, labeling, and handling dangerous goods at work.
The 2025 update strengthens training, documentation, and hazard communication rules.
These rules apply across Canada and are enforced by provincial and federal workplace safety regulators.
Employer Responsibility Under WHMIS
Employers are legally required to create and maintain a safe workplace. This includes:
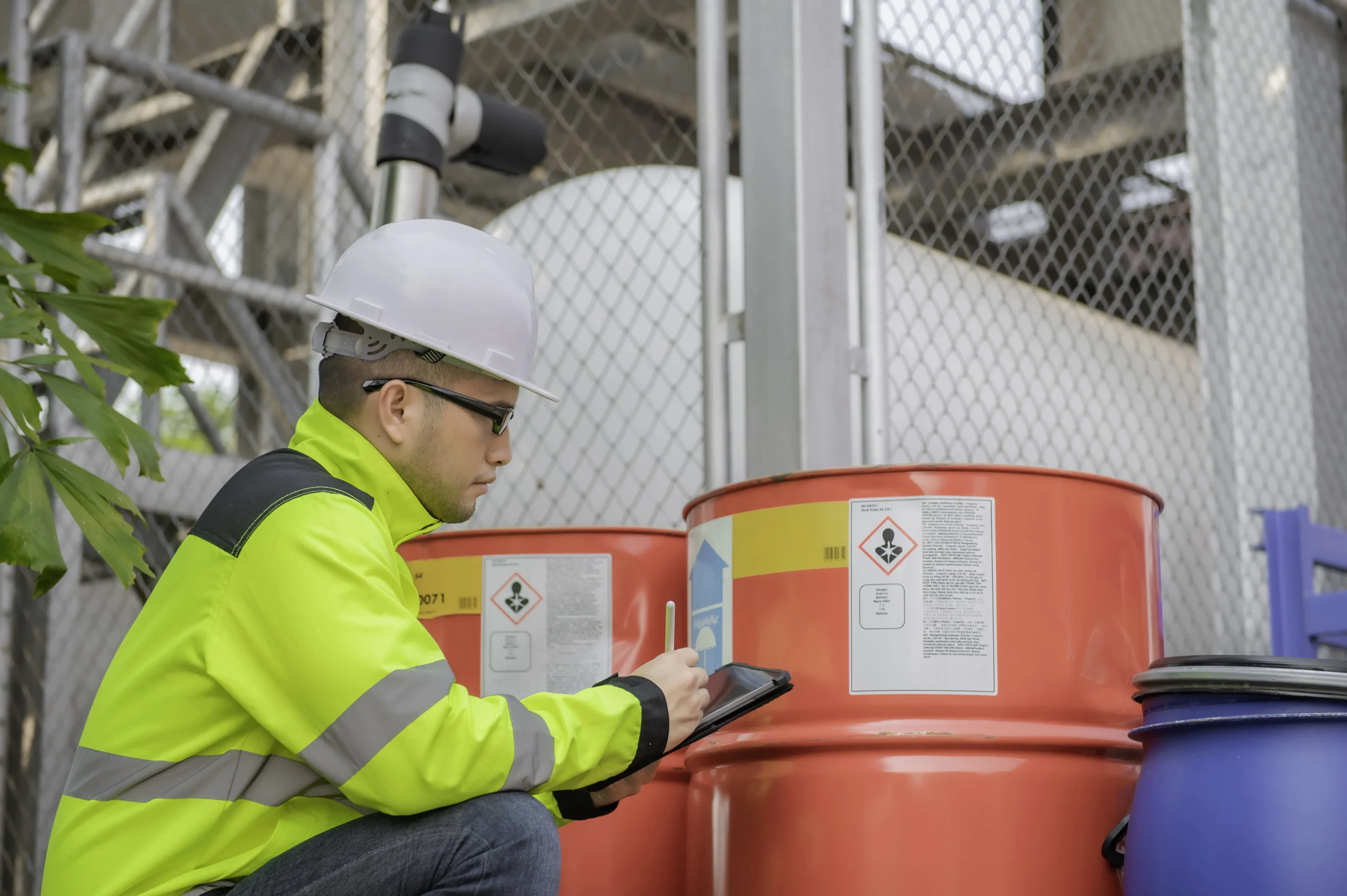
- Identifying hazardous materials in the workplace.
- Ensuring labels are accurate and updated according to WHMIS 2025.
- Maintaining up-to-date Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for every hazardous product.
- Providing ongoing training for all employees who work with or near hazardous products.
- Reviewing and updating WHMIS procedures annually or when new hazards are introduced.
In short, the employer responsibility under WHMIS is about prevention, communication, and training — not just reaction after an incident.

Employer WHMIS Training Obligations
WHMIS 2025 places a strong emphasis on training. Employers must:
- Deliver initial WHMIS training to new hires before they start working with hazardous materials.
- Provide refresher training annually or when work conditions change.
- Keep training records for each employee, documenting dates, topics covered, and test results.
- Ensure training is specific to the workplace, not just generic online modules.
Example:
An automotive repair shop can’t rely on a generic WHMIS course alone. Workers must be trained on the actual chemicals they use — like brake cleaner, battery acid, and solvents — and how to handle spills or exposure.
Employee Responsibilities Under WHMIS
While this article focuses on employers, it’s important to note that workers have a role too.
Employee responsibilities under WHMIS include:
- Participating in WHMIS training.
- Following safe work procedures.
- Wearing required protective equipment.
- Reporting missing or damaged labels.
- Reporting hazardous incidents immediately.
A safety program works only if both sides follow their responsibilities.
WHMIS 2025 Compliance Requirements: The Details
To remain compliant, employers must:
- Inventory All Hazardous Products
Keep a complete list of every controlled product in the workplace. - Label Every Container
From spray bottles to large drums, all containers must be clearly labeled according to WHMIS 2025 standards. - Maintain Current SDS
Safety Data Sheets must be readily accessible and less than 3 years old. - Document Training
Keep records for inspections and potential legal reviews. - Perform Hazard Assessments
Regularly review job tasks to identify new risks.
Real-World WHMIS Enforcement Examples
Case 1 – Ontario Manufacturing Plant
In 2023, a metal fabrication company was fined $35,000 after a worker suffered chemical burns from mislabeled containers. The investigation revealed the employer had not updated SDS records in over five years and had provided no refresher training since 2017.
Case 2 – Alberta Construction Site
In 2024, a contractor was issued a stop-work order for failing to provide WHMIS training to temporary workers handling epoxy resins. The delay in compliance cost the company nearly $50,000 in lost productivity and penalties.
These cases show how failing to meet WHMIS 2025 compliance requirements can quickly become costly.

Common Mistakes Employers Make
- Assuming WHMIS training is a “one-and-done” process.
- Using outdated SDS or keeping them in inaccessible locations.
- Neglecting to label secondary containers (e.g., spray bottles).
- Relying on generic WHMIS modules that don’t address actual workplace hazards.
Avoid these mistakes by setting clear policies, tracking updates, and scheduling annual compliance reviews.
Why This Matters
Aside from legal compliance, a strong WHMIS program:
- Prevents injuries and illnesses.
- Reduces downtime from accidents.
- Protects your company’s reputation.
- Demonstrates a commitment to worker safety.
Neglecting your employer WHMIS training obligations is not just risky — it’s a signal to workers that safety isn’t a priority.
Thought-Provoking Question
If your workplace was inspected today, would you feel confident handing over your WHMIS records — or would you be scrambling to cover gaps?
FAQs:
Key Takeaways
- Employer responsibility under WHMIS includes hazard identification, training, and record-keeping.
- Employer WHMIS training obligations require workplace-specific instruction and annual refreshers.
- WHMIS 2025 increases accountability, and non-compliance can lead to significant financial and legal consequences.